How to Detect Player Emulators in iOS Apps Using AI
This Knowledge Base article describes how to use Appdome’s AI/ML in your CI/CD pipeline to continuously deliver plugins that Detect App Players in iOS apps.
What Are iOS Game Emulators?
iOS app players, often referred to as emulators or simulators, allow iOS apps to run in non-native environments such as PCs or Macs. Tools like Appetize.io and iPadian enable users to mimic iOS environments but are frequently limited by Apple’s ecosystem controls. While commonly used for testing, attackers exploit these platforms to bypass app security, manipulate functionality, and identify vulnerabilities, risking user data and app integrity. Detecting and preventing unauthorized use of iOS app players is essential for safeguarding sensitive data, ensuring app functionality as intended, and maintaining compliance with data protection standards.
How Appdome Protects Mobile Apps Against iOS Game Emulators?
Appdome’s dynamic Detect iOS App Player plugin identifies unauthorized attempts to run iOS apps in emulated or simulated environments. By detecting tools like Appetize.io and iPadian, the plugin blocks these threats, ensuring app integrity and preventing data exposure. Mobile developers can leverage Appdome’s Threat-Events™ to gather actionable data on iOS app player activity and create customized user responses when such threats are detected.
Prerequisites for Using Appdome's Detect App Players Plugins:
To use Appdome’s mobile app security build system to Detect App Players , you’ll need:
- Appdome account (create a free Appdome account here)
- A license for Detect App Players
- Mobile App (.ipa for iOS)
- Signing Credentials (see Signing Secure Android apps and Signing Secure iOS apps)
How to Implement Detect App Players in iOS Apps Using Appdome
On Appdome, follow these 3 simple steps to create self-defending iOS Apps that Detect App Players without an SDK or gateway:
-
Designate the Mobile App to be protected.
-
Upload an app via the Appdome Mobile Defense platform GUI or via Appdome’s DEV-API or CI/CD Plugins.
-
iOS Formats: .ipa
-
Detect App Players is compatible with: Obj-C, Java, Swift, Flutter, React Native, Unity, Xamarin, Cordova and other iOS apps.
-
-
Select the defense: Detect App Players.
-
-
Follow the steps in Sections 2.2-2.2.2 of this article to add the Detect App Players feature to your Fusion Set via the Appdome Console.
-
When you select the Detect App Players you'll notice that the Fusion Set you created in step 2.1 now bears the icon of the protection category that contains Detect App Players.

Figure 2: Fusion Set that displays the newly added Detect App Players protection
Note: Annotating the Fusion Set to identify the protection(s) selected is optional only (not mandatory). -
Open the Fusion Set Detail Summary by clicking the “...” symbol on the far-right corner of the Fusion Set. Copy the Fusion Set ID from the Fusion Set Detail Summary (as shown below):

Figure 3: Fusion Set Detail Summary
-
Follow the instructions below to use the Fusion Set ID inside any standard mobile DevOps or CI/CD toolkit like Bitrise, Jenkins, Travis, Team City, Circle CI or other system:
-
Refer to the Appdome API Reference Guide for API building instructions.
-
Look for sample APIs in Appdome’s GitHub Repository.
-
Create and name the Fusion Set (security template) that will contain the Detect App Players feature as shown below:
Figure 1: Fusion Set that will contain the Detect App Players feature
-
-
Add the Detect App Players feature to your security template.
-
Navigate to Build > Anti Fraud tab > Mobile Cheat Prevention section in the Appdome Console.
-
Toggle On Detect App Players.
(a) Choose to monitor this attack vector by checking the Threat Events checkbox associated with Detect App Players as shown below.
(b) To receive mobile Threat Monitoring, check the ThreatScope™ box as shown below. For more details, see our knowledge base article on ThreatScope™ Mobile XDR.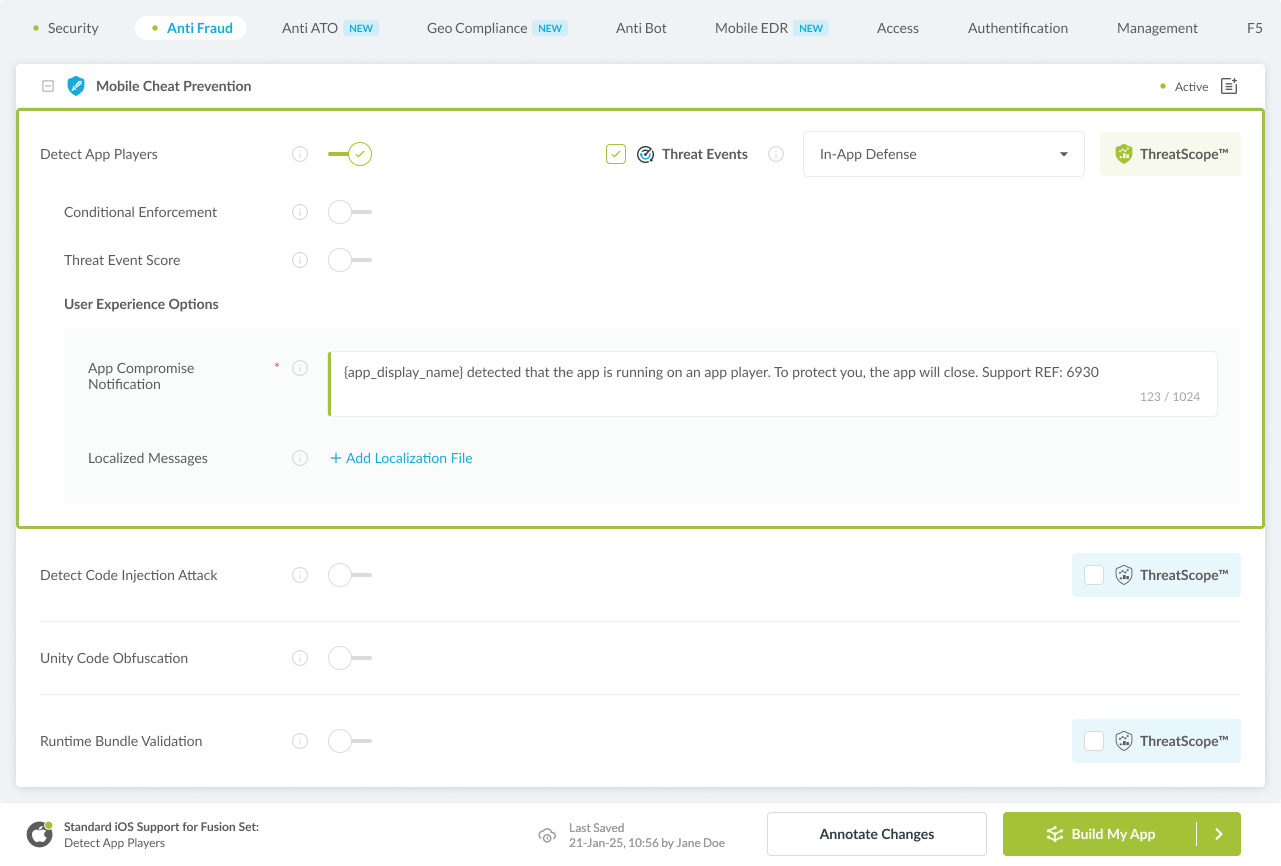
Figure 4: Selecting Detect App Players
Note: The Appdome Platform displays the Mobile Operation Systems supported by each defense in real-time. For more details, see our OS Support Policy KB. -
Select the Threat-Event™ in-app mobile Threat Defense and Intelligence policy for Detect App Players:
-
Threat-Events™ OFF > In-App Defense
If the Threat-Events™ setting is not selected. Appdome will detect and defend the user and app by enforcing App Players.
-
Threat-Events™ ON > In-App Detection
When this setting is used, Appdome detects the presence of App Players and passes Appdome’s Threat-Event™ attack intelligence to the app’s business logic for processing, enforcement, and user notification. For more information on consuming and using Appdome Threat-Events™ in the app, see section Using Threat-Events™ to Detect Detect App Players Intelligence and Control in Mobile Apps.
-
Threat-Events™ ON > In-App Defense
When this setting is used, Appdome detects and defends against App Players (same as Appdome Enforce) and passes Appdome’s Threat-Event™ attack intelligence to the app’s business logic for processing. For more information on consuming and using Appdome Threat-Events™ in the app, see section Using Threat-Events™ for Detect Detect App Players Intelligence and Control in Mobile Apps.
-
-
Configure the User Experience Options for Detect App Players:
With Threat-Events™ OFF, Appdome provides several user experience options for mobile brands and developers.- App Compromise Notification: Customize the pop-up or toast Appdome uses to notify the user when a threat is present while using the protected mobile app.
- Short message Option. This is available for mobile devices that allow a banner notification for security events.
-
Localized Message Option. Allows Appdome users to support global languages in security notifications.

Figure 5: Default User Experience Options for Appdome’s App Players
-
Detect App Players Threat Code™. Appdome uses AI/ML to generate a unique code each time Detect App Players is triggered by an active threat on the mobile device. Use the code in Appdome Threat Resolution Center™ to help end users identify, find and resolve active threats on the personal mobile devices.
-
Congratulations! The Detect App Players protection is now added to the mobile app -
-
Certify the Detect App Players feature in iOS Apps
After building Detect App Players, Appdome generates a Certified Secure™ certificate to guarantee that the Detect App Players protection has been added and is protecting the app. To verify that the Detect App Players protection has been added to the mobile app, locate the protection in the Certified Secure™ certificate as shown below:
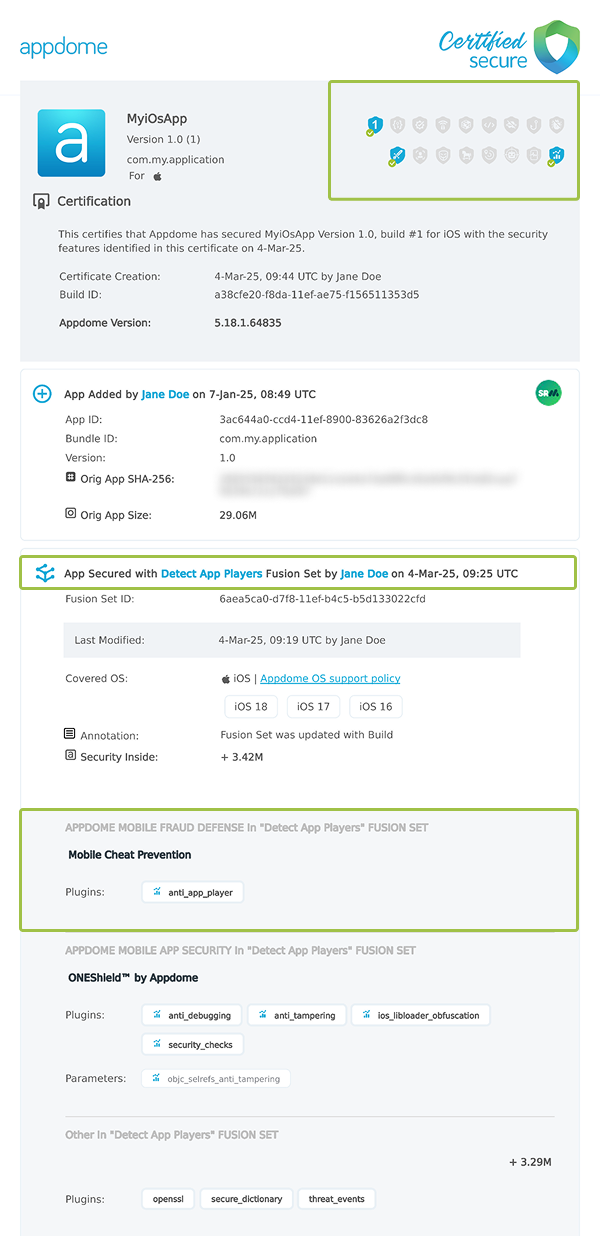
Figure 6: Certified Secure™ certificate
Each Certified Secure™ certificate provides DevOps and DevSecOps organizations the entire workflow summary, audit trail of each build, and proof of protection that Detect App Players has been added to each iOS app. Certified Secure provides instant and in-line DevSecOps compliance certification that Detect App Players and other mobile app security features are in each build of the mobile app.
Using Threat-Events™ for App Players Intelligence and Control in iOS Apps
Appdome Threat-Events™ provides consumable in-app mobile app attack intelligence and defense control when App Players is detected. To consume and use Threat-Events™ for App Players in iOS Apps, use AddObserverForName in Notification Center, and the code samples for Threat-Events™ for App Players shown below.
The specifications and options for Threat-Events™ for App Players are:
| Threat-Event™ Elements | Detect App Players Method Detail |
|---|---|
| Appdome Feature Name | Detect App Players |
| Threat-Event Mode | |
| OFF, IN-APP DEFENSE | Appdome detects, defends and notifies user (standard OS dialog) using customizable messaging. |
| ON, IN-APP DETECTION | Appdome detects the attack or threat and passes the event in a standard format to the app for processing (app chooses how and when to enforce). |
| ON, IN-APP DEFENSE | Uses Appdome Enforce mode for any attack or threat and passes the event in a standard format to the app for processing (gather intel on attacks and threats without losing any protection). |
| Certified Secure™ Threat Event Check | |
| Visible in ThreatScope™ | |
| Developer Parameters for Detecting App Players Threat-Event™ | |
| Threat-Event NAME | AppPlayerDetected |
| Threat-Event DATA | reasonData |
| Threat-Event CODE | reasonCode |
| Threat-Event REF | 6801 |
| Threat-Event SCORE | |
| currentThreatEventScore | Current Threat-Event score |
| threatEventsScore | Total Threat-events score |
| Threat-Event Context Keys | |
|---|---|
| message | Message displayed for the user on event |
| failSafeEnforce | Timed enforcement against the identified threat |
| externalID | The external ID of the event which can be listened via Threat Events |
| osVersion | OS version of the current device |
| deviceModel | Current device model |
| deviceManufacturer | The manufacturer of the current device |
| fusedAppToken | The task ID of the Appdome fusion of the currently running app |
| kernelInfo | Info about the kernel: system name, node name, release, version and machine. |
| deviceID | Current device ID |
| reasonCode | Reason code of the occurred event |
| buildDate | Appdome fusion date of the current application |
| devicePlatform | OS name of the current device |
| updatedOSVersion | Is the OS version up to date |
| timeZone | Time zone |
| deviceFaceDown | Is the device face down |
| locationLong | Location longitude conditioned by location permission |
| locationLat | Location latitude conditioned by location permission |
| locationState | Location state conditioned by location permission |
| wifiSsid | Wifi SSID |
| wifiSsidPermissionStatus | Wifi SSID permission status |
| threatCode | The last six characters of the threat code specify the OS, allowing the Threat Resolution Center to address the attack on the affected device. |
With Threat-Events™ enabled (turned ON), iOS developers can get detailed attack intelligence and granular defense control in iOS applications and create amazing user experiences for all mobile end users when App Players is detected.
The following is a code sample for native iOS apps, which uses all values in the specification above for Detect App Players:
Important! Replace all placeholder instances of <Context Key> with the specific name of your threat event context key across all language examples. This is crucial to ensure your code functions correctly with the intended event data. For example, The <Context Key> could be the message, externalID, OS Version, reason code, etc.
x
let center = NotificationCenter.defaultcenter.addObserver(forName: Notification.Name("AppPlayerDetected"), object: nil, queue: nil) { (note) in guard let usrInf = note.userInfo else { return } let message = usrInf["message"]; // Message shown to the user let reasonData = usrInf["reasonData"]; // Threat detection cause let reasonCode = usrInf["reasonCode"]; // Event reason code // Current threat event score let currentThreatEventScore = usrInf["currentThreatEventScore"]; // Total threat events score let threatEventsScore = usrInf["threatEventsScore"]; // Replace '<Context Key>' with your specific event context key // let variable = usrInf["<Context Key>"]; // Your logic goes here (Send data to Splunk/Dynatrace/Show Popup...)}Using Appdome, there are no development or coding prerequisites to build secured iOS Apps by using Detect App Players. There is no SDK and no library to code or implement in the app and no gateway to deploy in your network. All protections are built into each app and the resulting app is self-defending and self-protecting.
Releasing and Publishing Mobile Apps with Detect App Players
After successfully securing your app by using Appdome, there are several available options to complete your project, depending on your app lifecycle or workflow. These include:
- Customizing, Configuring & Branding Secure Mobile Apps.
- Deploying/Publishing Secure mobile apps to Public or Private app stores.
- Releasing Secured Android & iOS Apps built on Appdome.
Related Articles:
- How to Detect Player Emulators & Modding Platforms in Android Apps
- How Hackers Use Nox Emulator to Cheat Mobile Games
- How to Block Memory Editing tools for Android and iOS apps
- How to Prevent Android Apps from Running on Emulators
How Do I Learn More?
If you have any questions, please send them our way at support.appdome.com or via the chat window on the Appdome platform.
Thank you!
Thanks for visiting Appdome! Our mission is to secure every app on the planet by making mobile app security easy. We hope we’re living up to the mission with your project.
